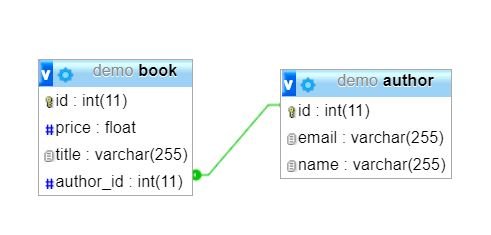
Sometime, you have to create the relationships among the various tables or entities when we work in database design. Like, if we consider Book and Author entities, there A book may belongs to one author, but a author can belong to many books.
Here is the hibernate example for this scnario.
package example.configuration.demo6;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Author{
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private int id;
private String name;
private String email;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
package example.configuration.demo6;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="book")
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private int id;
private String title;
private float price;
@ManyToOne
private Author author;
public float getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(float price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public Author getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(Author author) {
this.author = author;
}
}
package example.configuration.demo6;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args){
StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
SessionFactory factory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
Session session=factory.openSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
Author author=new Author();
author.setName("John");
author.setEmail("john@gmail.com");
Book book=new Book();
book.setTitle("Learning Hibernate");
book.setAuthor(author);
book.setPrice(2342);
session.save(author);
session.save(book);
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MariaDB53Dialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">create</property>
<property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property>
<property name="packagesToScan">example</property>
<mapping class="example.configuration.demo6.Book"/>
<mapping package="example"/>
<mapping class="example.configuration.demo6.Author"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
Here is the database design created by the above code example;